
For two-way ANOVA with no repeated measures: The denominator MS value is always the MSresidual.The MS value for the denominator depends on the experimental design. F ratioĮach F ratio is computed by dividing the MS value by another MS value. In other words, for each row in the ANOVA table divide the SS value by the df value to compute the MS value. Mean squaresĮach mean square value is computed by dividing a sum-of-squares value by the corresponding degrees of freedom. They say "B x S/A" where Prism says "residual", and say "S/A" where Prism says "subject". But note they use the term "A x B x S" where we say "Residual". Table 12.16 on page 595 explains the ANOVA table for repeated measures in one factor. Table 12.2 on page 576 explains the ANOVA table for repeated measures in both factors. When there are repeated measures for both factors, this value equals the number of subjects (3) minus 1, so df=2.ĭetails on how the SS and DF are computed can be found in Maxwell and Delaney (reference below). When the matched values are in the same row, there arr 6 subjects treated in two ways (one for each row), so df is 4. When the matched values are stacked, there are 9 subjects and three treatments, so df equals 6. The df for subjects is the number of subjects minus number of treatments.It is the same regardless of repeated measures.

How to conduct a two way anova in excel how to#
How to report two-way ANOVA results in a table Sum-of-squaresįocus first on the sum-of-squares (SS) column with no repeated measures: I rearranged and renamed a bit so the four can be shown on one table ( Excel file). Here are the ANOVA tables for the four conditions. The colors are repeated between tables, but this means nothing. Each color within a table represents one subject.
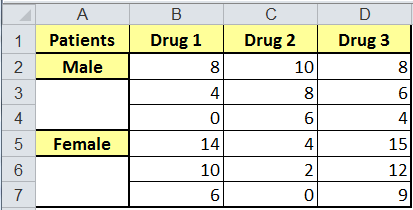
The tables below are color coded to explain these designs. I analyzed the data four ways: assuming no repeated measures, assuming repeated measures with matched values stacked, assuming repeated measures with matched values spread across a row, and with repeated measures in both directions. I entered data with two rows, three columns, and three side-by-side replicates per cell. But if you are curious in the details, this page explains how the ANOVA table is calculated. You can interpret the results of two-way ANOVA by looking at the P values, and especially at multiple comparisons.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
